In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.[1] It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The same amount of work is done by the body in decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest.
In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass m traveling at a speed v is  . In relativistic mechanics, this is a good approximation only when v is much less than the speed of light.
. In relativistic mechanics, this is a good approximation only when v is much less than the speed of light.
 . In relativistic mechanics, this is a good approximation only when v is much less than the speed of light.
. In relativistic mechanics, this is a good approximation only when v is much less than the speed of light.History and etymology[edit]
The adjective kinetic has its roots in the Greek word κίνησις kinesis, meaning "motion". The dichotomy between kinetic energy andpotential energy can be traced back to Aristotle's concepts of actuality and potentiality.[citation needed]
The principle in classical mechanics that E ∝ mv² was first developed by Gottfried Leibniz and Johann Bernoulli, who described kinetic energy as the living force, vis viva. Willem 's Gravesande of the Netherlands provided experimental evidence of this relationship. By dropping weights from different heights into a block of clay, Willem 's Gravesande determined that their penetration depth was proportional to the square of their impact speed. Émilie du Châtelet recognized the implications of the experiment and published an explanation.[2]
The terms kinetic energy and work in their present scientific meanings date back to the mid-19th century. Early understandings of these ideas can be attributed to Gaspard-Gustave Coriolis, who in 1829 published the paper titled Du Calcul de l'Effet des Machinesoutlining the mathematics of kinetic energy. William Thomson, later Lord Kelvin, is given the credit for coining the term "kinetic energy" c. 1849–51.[3][4]
Introduction[edit]
Energy occurs in many forms, including chemical energy, thermal energy, electromagnetic radiation, gravitational energy, electric energy, elastic energy, nuclear energy, and rest energy. These can be categorized in two main classes: potential energy and kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy may be best understood by examples that demonstrate how it is transformed to and from other forms of energy. For example, a cyclist uses chemical energy provided by food to accelerate a bicycle to a chosen speed. On a level surface, this speed can be maintained without further work, except to overcome air resistance and friction. The chemical energy has been converted into kinetic energy, the energy of motion, but the process is not completely efficient and produces heat within the cyclist.
The kinetic energy in the moving cyclist and the bicycle can be converted to other forms. For example, the cyclist could encounter a hill just high enough to coast up, so that the bicycle comes to a complete halt at the top. The kinetic energy has now largely been converted to gravitational potential energy that can be released by freewheeling down the other side of the hill. Since the bicycle lost some of its energy to friction, it never regains all of its speed without additional pedaling. The energy is not destroyed; it has only been converted to another form by friction. Alternatively the cyclist could connect a dynamo to one of the wheels and generate some electrical energy on the descent. The bicycle would be traveling slower at the bottom of the hill than without the generator because some of the energy has been diverted into electrical energy. Another possibility would be for the cyclist to apply the brakes, in which case the kinetic energy would be dissipated through friction as heat.
Like any physical quantity that is a function of velocity, the kinetic energy of an object depends on the relationship between the object and the observer's frame of reference. Thus, the kinetic energy of an object is not invariant.
Spacecraft use chemical energy to launch and gain considerable kinetic energy to reach orbital velocity. In a perfectly circular orbit, this kinetic energy remains constant because there is almost no friction in near-earth space. However it becomes apparent at re-entry when some of the kinetic energy is converted to heat. If the orbit is elliptical or hyperbolic, then throughout the orbit kinetic and potential energy are exchanged; kinetic energy is greatest and potential energy lowest at closest approach to the earth or other massive body, while potential energy is greatest and kinetic energy the lowest at maximum distance. Without loss or gain, however, the sum of the kinetic and potential energy remains constant.
Kinetic energy can be passed from one object to another. In the game of billiards, the player imposes kinetic energy on the cue ball by striking it with the cue stick. If the cue ball collides with another ball, it slows down dramatically and the ball it collided with accelerates to a speed as the kinetic energy is passed on to it. Collisions in billiards are effectivelyelastic collisions, in which kinetic energy is preserved. In inelastic collisions, kinetic energy is dissipated in various forms of energy, such as heat, sound, binding energy (breaking bound structures).
Flywheels have been developed as a method of energy storage. This illustrates that kinetic energy is also stored in rotational motion.
Several mathematical descriptions of kinetic energy exist that describe it in the appropriate physical situation. For objects and processes in common human experience, the formula ½mv² given by Newtonian (classical) mechanics is suitable. However, if the speed of the object is comparable to the speed of light, relativistic effects become significant and the relativistic formula is used. If the object is on the atomic or sub-atomic scale, quantum mechanical effects are significant and a quantum mechanical model must be employed.
Newtonian kinetic energy[edit]
Kinetic energy of rigid bodies[edit]
In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a point object (an object so small that its mass can be assumed to exist at one point), or a non-rotating rigid body depends on themass of the body as well as its speed. The kinetic energy is equal to the mass multiplied by the square of the speed, multiplied by the constant 1/2. In formula form:
where 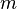 is the mass and
is the mass and  is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.
is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.
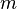 is the mass and
is the mass and  is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.
is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.
For example, one would calculate the kinetic energy of an 80 kg mass (about 180 lbs) traveling at 18 metres per second (about 40 mph, or 65 km/h) as
When you throw a ball, you do work on it to give it speed as it leaves your hand. The moving ball can then hit something and push it, doing work on what it hits. The kinetic energy of a moving object is equal to the work required to bring it from rest to that speed, or the work the object can do while being brought to rest: net force × displacement = kinetic energy, i.e.,
Since the kinetic energy increases with the square of the speed, an object doubling its speed has four times as much kinetic energy. For example, a car traveling twice as fast as another requires four times as much distance to stop, assuming a constant braking force. As a consequence of this quadrupling, it takes four times the work to double the speed.
The kinetic energy of an object is related to its momentum by the equation:
where:
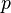 is momentum
is momentum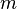 is mass of the body
is mass of the body
For the translational kinetic energy, that is the kinetic energy associated with rectilinear motion, of a rigid body with constant mass 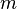 , whose center of mass is moving in a straight line with speed
, whose center of mass is moving in a straight line with speed 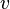 , as seen above is equal to
, as seen above is equal to
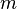 , whose center of mass is moving in a straight line with speed
, whose center of mass is moving in a straight line with speed 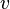 , as seen above is equal to
, as seen above is equal to
where:
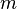 is the mass of the body
is the mass of the body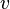 is the speed of the center of mass of the body.
is the speed of the center of mass of the body.
The kinetic energy of any entity depends on the reference frame in which it is measured. However the total energy of an isolated system, i.e. one in which energy can neither enter nor leave, does not change over time in the reference frame in which it is measured. Thus, the chemical energy converted to kinetic energy by a rocket engine is divided differently between the rocket ship and its exhaust stream depending upon the chosen reference frame. This is called the Oberth effect. But the total energy of the system, including kinetic energy, fuel chemical energy, heat, etc., is conserved over time, regardless of the choice of reference frame. Different observers moving with different reference frames would however disagree on the value of this conserved energy.
The kinetic energy of such systems depends on the choice of reference frame: the reference frame that gives the minimum value of that energy is the center of momentumframe, i.e. the reference frame in which the total momentum of the system is zero. This minimum kinetic energy contributes to the invariant mass of the system as a whole.
Derivation[edit]
The work done accelerating a particle during the infinitesimal time interval dt is given by the dot product of force and displacement:
where we have assumed the relationship p = m v. (However, also see the special relativistic derivation below.)
Applying the product rule we see that:
Therefore (assuming constant mass so that dm=0), the following can be seen:
Since this is a total differential (that is, it only depends on the final state, not how the particle got there), we can integrate it and call the result kinetic energy. Assuming the object was at rest at time 0, we integrate from time 0 to time t because the work done by the force to bring the object from rest to velocity v is equal to the work necessary to do the reverse:
This equation states that the kinetic energy (Ek) is equal to the integral of the dot product of the velocity (v) of a body and the infinitesimal change of the body's momentum (p). It is assumed that the body starts with no kinetic energy when it is at rest (motionless).
Rotating bodies[edit]
If a rigid body Q is rotating about any line through the center of mass then it has rotational kinetic energy ( ) which is simply the sum of the kinetic energies of its moving parts, and is thus given by:
) which is simply the sum of the kinetic energies of its moving parts, and is thus given by:
 ) which is simply the sum of the kinetic energies of its moving parts, and is thus given by:
) which is simply the sum of the kinetic energies of its moving parts, and is thus given by:
where:
- ω is the body's angular velocity
- r is the distance of any mass dm from that line
 is the body's moment of inertia, equal to
is the body's moment of inertia, equal to  .
.
(In this equation the moment of inertia must be taken about an axis through the center of mass and the rotation measured by ω must be around that axis; more general equations exist for systems where the object is subject to wobble due to its eccentric shape).
Kinetic energy of systems[edit]
A system of bodies may have internal kinetic energy due to the relative motion of the bodies in the system. For example, in the Solar System the planets and planetoids are orbiting the Sun. In a tank of gas, the molecules are moving in all directions. The kinetic energy of the system is the sum of the kinetic energies of the bodies it contains.
A macroscopic body that is stationary (i.e. a reference frame has been chosen to correspond to the body's center of momentum) may have various kinds of internal energy at the molecular or atomic level, which may be regarded as kinetic energy, due to molecular translation, rotation, and vibration, electron translation and spin, and nuclear spin. These all contribute to the body's mass, as provided by the special theory of relativity. When discussing movements of a macroscopic body, the kinetic energy referred to is usually that of the macroscopic movement only. However all internal energies of all types contribute to body's mass, inertia, and total energy.
Frame of reference[edit]
The speed, and thus the kinetic energy of a single object is frame-dependent (relative): it can take any non-negative value, by choosing a suitable inertial frame of reference. For example, a bullet passing an observer has kinetic energy in the reference frame of this observer. The same bullet is stationary from the point of view of an observer moving with the same velocity as the bullet, and so has zero kinetic energy.[5] By contrast, the total kinetic energy of a system of objects cannot be reduced to zero by a suitable choice of the inertial reference frame, unless all the objects have the same velocity. In any other case the total kinetic energy has a non-zero minimum, as no inertial reference frame can be chosen in which all the objects are stationary. This minimum kinetic energy contributes to the system's invariant mass, which is independent of the reference frame.
The total kinetic energy of a system depends on the inertial frame of reference: it is the sum of the total kinetic energy in a center of momentum frame and the kinetic energy the total mass would have if it were concentrated in the center of mass.
This may be simply shown: let  be the relative velocity of the center of mass frame i in the frame k. Since
be the relative velocity of the center of mass frame i in the frame k. Since 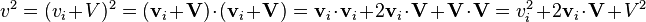 ,
,
 be the relative velocity of the center of mass frame i in the frame k. Since
be the relative velocity of the center of mass frame i in the frame k. Since 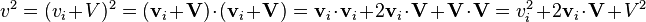 ,
,
However, let  the kinetic energy in the center of mass frame,
the kinetic energy in the center of mass frame,  would be simply the total momentum that is by definition zero in the center of mass frame, and let the total mass:
would be simply the total momentum that is by definition zero in the center of mass frame, and let the total mass: 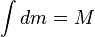 . Substituting, we get:[6]
. Substituting, we get:[6]
 the kinetic energy in the center of mass frame,
the kinetic energy in the center of mass frame,  would be simply the total momentum that is by definition zero in the center of mass frame, and let the total mass:
would be simply the total momentum that is by definition zero in the center of mass frame, and let the total mass: 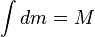 . Substituting, we get:[6]
. Substituting, we get:[6]
Thus the kinetic energy of a system is lowest with respect to center of momentum reference frames, i.e., frames of reference in which the center of mass is stationary (either thecenter of mass frame or any other center of momentum frame). In any other frame of reference there is additional kinetic energy corresponding to the total mass moving at the speed of the center of mass. The kinetic energy of the system in the center of momentum frame is a quantity that is both invariant (all observers see it to be the same) and is conserved (in an isolated system, it cannot change value, no matter what happens inside the system).
Rotation in systems[edit]
It sometimes is convenient to split the total kinetic energy of a body into the sum of the body's center-of-mass translational kinetic energy and the energy of rotation around the center of mass (rotational energy):
where:
- Ek is the total kinetic energy
- Et is the translational kinetic energy
- Er is the rotational energy or angular kinetic energy in the rest frame
Thus the kinetic energy of a tennis ball in flight is the kinetic energy due to its rotation, plus the kinetic energy due to its translation.
Relativistic kinetic energy of rigid bodies[edit]
In special relativity, we must change the expression for linear momentum.
Using m for rest mass, v and v for the object's velocity and speed respectively, and c for the speed of light in vacuum, we assume for linear momentum that  , where
, where 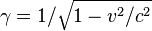 .
.
 , where
, where 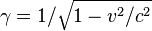 .
.
Integrating by parts gives
Remembering that 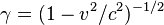 , we get:
, we get:
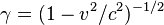 , we get:
, we get:
where E0 serves as an integration constant. Thus:
The constant of integration E0 is found by observing that, when  and
and  , giving
, giving
 and
and  , giving
, giving
and giving the usual formula:
If a body's speed is a significant fraction of the speed of light, it is necessary to use relativistic mechanics (the theory of relativity as developed by Albert Einstein) to calculate its kinetic energy.
For a relativistic object the momentum p is equal to:
Thus the work expended accelerating an object from rest to a relativistic speed is:
The equation shows that the energy of an object approaches infinity as the velocity v approaches the speed of light c, thus it is impossible to accelerate an object across this boundary.
The mathematical by-product of this calculation is the mass-energy equivalence formula—the body at rest must have energy content equal to:
At a low speed (v<<c), the relativistic kinetic energy may be approximated well by the classical kinetic energy. This is done by binomial approximation. Indeed, taking Taylor expansion for the reciprocal square root and keeping first two terms we get:
So, the total energy E can be partitioned into the energy of the rest mass plus the traditional Newtonian kinetic energy at low speeds.
When objects move at a speed much slower than light (e.g. in everyday phenomena on Earth), the first two terms of the series predominate. The next term in the approximation is small for low speeds, and can be found by extending the expansion into a Taylor series by one more term:
For example, for a speed of 10 km/s (22,000 mph) the correction to the Newtonian kinetic energy is 0.0417 J/kg (on a Newtonian kinetic energy of 50 MJ/kg) and for a speed of 100 km/s it is 417 J/kg (on a Newtonian kinetic energy of 5 GJ/kg), etc.
For higher speeds, the formula for the relativistic kinetic energy[7] is derived by simply subtracting the rest mass energy from the total energy:
The relation between kinetic energy and momentum is more complicated in this case, and is given by the equation:
This can also be expanded as a Taylor series, the first term of which is the simple expression from Newtonian mechanics.
What this suggests is that the formulas for energy and momentum are not special and axiomatic, but rather concepts that emerge from the equation of mass with energy and the principles of relativity.
General relativity[edit]
See also: Schwarzschild geodesics
Using the convention that
where the four-velocity of a particle is
and  is the proper time of the particle, there is also an expression for the kinetic energy of the particle in general relativity.
is the proper time of the particle, there is also an expression for the kinetic energy of the particle in general relativity.
 is the proper time of the particle, there is also an expression for the kinetic energy of the particle in general relativity.
is the proper time of the particle, there is also an expression for the kinetic energy of the particle in general relativity.
If the particle has momentum
as it passes by an observer with four-velocity uobs, then the expression for total energy of the particle as observed (measured in a local inertial frame) is
and the kinetic energy can be expressed as the total energy minus the rest energy:
Consider the case of a metric that is diagonal and spatially isotropic (gtt,gss,gss,gss). Since
where vα is the ordinary velocity measured w.r.t. the coordinate system, we get
Solving for ut gives
Thus for a stationary observer (v= 0)
and thus the kinetic energy takes the form
Factoring out the rest energy gives:
This expression reduces to the special relativistic case for the flat-space metric where
In the Newtonian approximation to general relativity
where Φ is the Newtonian gravitational potential. This means clocks run slower and measuring rods are shorter near massive bodies.
Kinetic energy in quantum mechanics[edit]
Further information: Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, observables like kinetic energy are represented as operators. For one particle of mass m, the kinetic energy operator appears as a term in theHamiltonian and is defined in terms of the more fundamental momentum operator  as
as
 as
as
Notice that this can be obtained by replacing 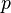 by
by  in the classical expression for kinetic energy in terms of momentum,
in the classical expression for kinetic energy in terms of momentum,
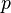 by
by  in the classical expression for kinetic energy in terms of momentum,
in the classical expression for kinetic energy in terms of momentum,
In the Schrödinger picture,  takes the form
takes the form 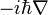 where the derivative is taken with respect to position coordinates and hence
where the derivative is taken with respect to position coordinates and hence
 takes the form
takes the form 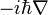 where the derivative is taken with respect to position coordinates and hence
where the derivative is taken with respect to position coordinates and hence
The expectation value of the electron kinetic energy, 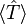 , for a system of N electrons described by the wavefunction
, for a system of N electrons described by the wavefunction 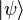 is a sum of 1-electron operator expectation values:
is a sum of 1-electron operator expectation values:
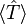 , for a system of N electrons described by the wavefunction
, for a system of N electrons described by the wavefunction 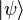 is a sum of 1-electron operator expectation values:
is a sum of 1-electron operator expectation values:
where 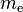 is the mass of the electron and
is the mass of the electron and 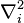 is the Laplacian operator acting upon the coordinates of the ith electron and the summation runs over all electrons.
is the Laplacian operator acting upon the coordinates of the ith electron and the summation runs over all electrons.
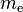 is the mass of the electron and
is the mass of the electron and 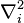 is the Laplacian operator acting upon the coordinates of the ith electron and the summation runs over all electrons.
is the Laplacian operator acting upon the coordinates of the ith electron and the summation runs over all electrons.
The density functional formalism of quantum mechanics requires knowledge of the electron density only, i.e., it formally does not require knowledge of the wavefunction. Given an electron density 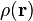 , the exact N-electron kinetic energy functional is unknown; however, for the specific case of a 1-electron system, the kinetic energy can be written as
, the exact N-electron kinetic energy functional is unknown; however, for the specific case of a 1-electron system, the kinetic energy can be written as
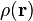 , the exact N-electron kinetic energy functional is unknown; however, for the specific case of a 1-electron system, the kinetic energy can be written as
, the exact N-electron kinetic energy functional is unknown; however, for the specific case of a 1-electron system, the kinetic energy can be written as
where ![T[\rho]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/b/0/3/b03e2e33686044e5f78fe6df092b3bd0.png) is known as the von Weizsäcker kinetic energy functional.
is known as the von Weizsäcker kinetic energy functional.
![T[\rho]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/b/0/3/b03e2e33686044e5f78fe6df092b3bd0.png) is known as the von Weizsäcker kinetic energy functional.
is known as the von Weizsäcker kinetic energy functional.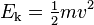

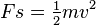





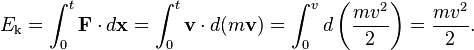


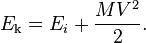


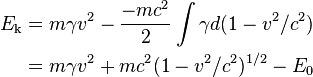


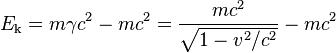









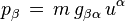
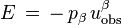
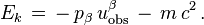

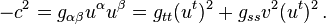



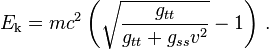





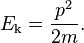


![T[\rho] = \frac{1}{8} \int \frac{ \nabla \rho(\mathbf{r}) \cdot \nabla \rho(\mathbf{r}) }{ \rho(\mathbf{r}) } d^3r](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/f/5/2/f527c2275e20ee9262c65527e0d16fe9.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment